
Search engine optimization is one of the most important aspects of a website’s performance as it determines how visible your website is on search engines such as Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and others.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is one of the most important aspects of website performance as it determines how visible it is in search on engines such as Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and others.
The right SEO strategy can help make your site more visible to users and drive more relevant traffic. This article is for you if you are a web developer who creates web pages or optimizes them for better performance and user experience. We will look at some tips to help you improve SEO on websites you build or optimize.
Should web developers know SEO?
SEO is a set of online marketing practices that help boost web development efforts and improve the website’s rankings. By optimizing a site’s content and metadata, companies can improve their chances of appearing higher in search engine result pages (SERP) when users enter key terms into Google or other search engines.
There are two main types of SEO: on-page SEO and off-page SEO.
- On-page SEO refers to optimizing a site’s content to meet the needs of search engines crawlers and users.
- Off-page SEO refers to efforts to attract Google’s attention through paid advertising campaigns or other means, like submitting content to directories.
The part that you can influence as a web developer is on-page SEO.
Even web developers who don’t have a strong background in digital marketing can learn enough to contribute value to projects by researching best practices and writing quality content that naturally ranks well in search. Why not add something extra to your web development process?
So here it is: a guide that explains the basics of technical SEO for web developers.
How do search engines work?
Search engines crawl the internet and collect data on web pages they store in their databases. When you enter a search query into a search engine, it looks through its database of website information and compares it to the content on your web page. If there is a match, it displays a list of results in order of relevance.
There are two main components to search engines: indexing and ranking.
- Indexing is the process of building a database of web pages containing relevant keywords and organizing them into “categories”.
- Ranking is putting those pages in order based on a set of rules so that the most relevant ones appear first.
It’s important to note that there are more search engines on the internet than just Google, but since this one is the most popular in the world, this article will focus mainly on optimizing for Google search results and draw from their guidelines for web developers.
How do you influence SEO as a web developer?
A significant portion of SEO focuses on the content, the selection of keywords, and the backlinks that web developers usually don’t deal with. However, there are aspects of SEO that, as web developers, you should keep in mind, and thanks to which the pages you create will be better visible in Google search results and other places.
Site structure
The website’s structure should be planned so that the users can easily and quickly find the information they are looking for. Make sure that the most important pages can be found with 2-3 clicks. This will flatten the website structure and users will not keep getting lost in the maze of random subpages.
Technical analysis
This is the part you will take care of when your website is ready. You’ll need one of page analysis tools – we use Ahrefs, but sometimes we add Semrush to that as well.
After creating an account and connecting the site, you will receive regular emails with a list of elements to improve. These can be broken images, duplicate content, missing meta tags, markup errors, and many others, with a description of where the error occurs (on which subpages) and how to fix it. You can also check the issues list in the tool panel at any time.
Additionally, Ahrefs and Semrush give you an overall webpage health score, so that you know if you are going in the right direction. Try using these tools, especially when making significant changes to the website.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a tool that allows you to check the performance of your website. And by performance, I mean how many people see your site in the search results, what its average position is, and how the number of clicks from the SERP has changed overtime. Additionally, you can see if all subpages are correctly indexed. And what is especially important for more complex websites – you can manually upload a sitemap.
The last thing that I want to discuss in this section is the Core Web Vitals report. If you enter this section, you can check if your website loads properly and fast enough for desktop and mobile – this affects the page’s ranking, but it is also essential for the user experience. So if site speed is crucial for both SEO and UX, it’s really worth checking out!
With Interaction to Next Paint (INP) becoming a stable Core Web Vital in 2024, there has been a change to what the three main components of Core Web Vitals are now:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – shows the perceived load speed, where the page’s main body is likely to be loaded.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – measures unexpected shifts of elements on the page.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – shows the longest latency of an interaction with the website.
You can learn more about Core Web Vitals here.
Page Speed Insights
Thanks to this tool, you can check how fast your website and its individual elements load. You will also see suggestions on how to improve page load parameters.
Sitemap
A sitemap is a text file with a list of all subpages, files, and generally all content on the website. It also provides information about the relationships between the individual elements on the page.
A sitemap lets Google know where to look for important parts of the site and provides additional information about the content, like publication date, alternate language versions, or video duration. It also provides information about changes to the website, errors, and generally helps search engine robots navigate your site.
Do I have to use a sitemap?
Suppose your website is not very complex and has good navigation (meaning that all important subpages are accessible from navigation or links on the subpages – reference the paragraph about page structure I mentioned earlier). In that case, Googlebot should find most places on your website by itself. If you know that your website is going to grow, or if it’s already large to begin with, it has an extensive archive of content, or many files like images and videos – a sitemap can help you a lot.
The general idea is that the structured data in your sitemap will make Googlebot’s job easier; thus, your website SEO can improve more or faster than without a sitemap.
Read how to prepare and load your sitemap here.
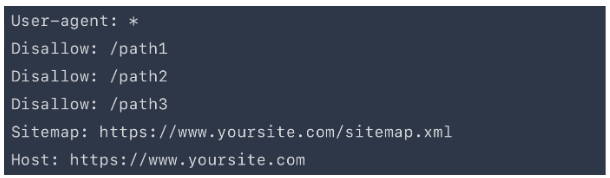
Robots.txt
This file tells the engines where they can and cannot enter, so if something is not to be indexed (e.g., 404, privacy policy, cart page, logins) – a robots.txt file is a good idea.
However, Google documentation says this is not the best way to hide selected subpages from the Google robot, but only to help prevent overloading the page with requests. It may happen that other sites will link to the subpage you want to hide, and then Google bot will index it anyway.
If you want to be sure that the selected subpage won’t be displayed in the search results, use the noindex meta tag.
Redirects
Every time you change your URLs, you should set up appropriate 301 redirects. Otherwise, search engines may remove changed or deleted addresses from their indexes.
Everyone who enters the old address will be redirected to the new page, and the search engines will index the new addresses after some time.
What redirects to use?
You will probably use one of the following two types of redirect most often:
- 301 redirect for pages that you permanently move to the new address,
- 302 redirects for pages that you move to the new URL only for a while.
Meta tags
Meta tags are a good way to give the Google bot additional information about your page. The two most important tags are meta title and meta description. This is what the user sees when viewing the search results. And although Google can change your meta tags if it finds other content from the subpage more appropriate, it is still always worth providing the text of your choice.
You can find a full list of meta tags that the Google bot understands here.
Schema markup
This is a piece of code that helps the search engines better understand the content through structured data. You can add it manually or generate it using a plug-in or a generator. Want to get more organic traffic, boost your website’s SEO, and make it appear in search as more than just a title and a piece of description? Enrich your SEO checklist with the use of schema markup.
You can write your schema yourself, but if you want to use a tool for that, check out this extension.
Open Graph
Open Graph is a kind of a special snippet of code for correctly displaying your page’s content on social media. Maybe it’s not exactly SEO, but it affects how the website’s content looks after it’s shared on social media, and if you optimize the website, it is also worth taking care of this part.
Below I am throwing an example of these HTML tags from one of our subpages:
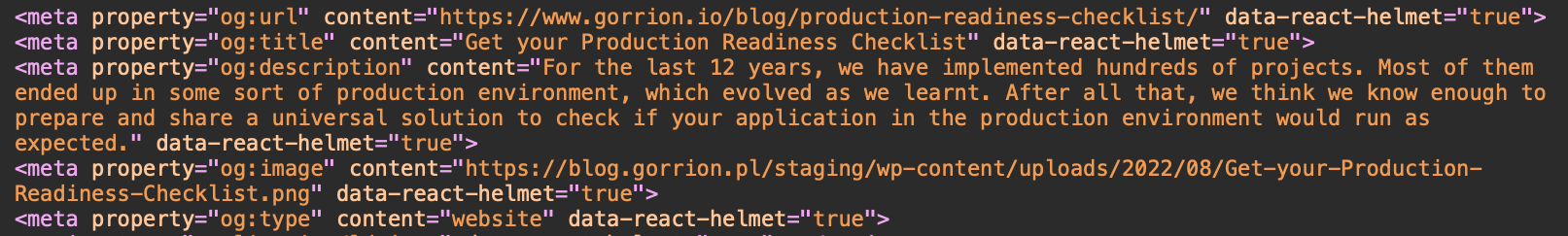
The use of Open Graph will make it easier and faster for social media users to understand what your content is about. Additionally, Facebook will be able to better identify what you are sharing and increase its visibility.
Broken links
Your website should not contain broken links, that is, links that lead to pages that no longer exist or have been changed. It’s a dead end for the search engine bot and will hurt your efforts to improve the site’s SEO. Also, it’s harmful to the UX as the users will bounce off the non-existent subpage.
Want to quickly check if you have any broken links on your page? Here you will find a free tool from Ahrefs.
Internal links
Do you have an influence on internal linking? If yes, make sure that your pages link to each other. You will make the bot’s work easier, and users will be able to find the information they are interested in. Just remember to keep the website structure as flat as possible and not to introduce unnecessary chaos.
Google also pays attention to the anchor text of your link, so make sure you use specific keywords in your internal links instead of the usual “click here.”
As an example, I will leave here a link to our article on the product readiness checklist. (See what I did there?)
Canonicals
Avoid duplicate content with canonical links. The rel=”canonical” HTML tags allow you to mark the main version of pages with repeated content. This means that you should use canonicals to avoid indexing problems if you have several subpages with the same content.
Not so obvious SEO basics
Below are 3 points that you may have read about many times. However, I know they are sometimes forgotten, so remember to include them in your to-do list when optimizing your website.
Creating URLs
Remember to take care of the URLs when building your page. They should be readable not only for you but mainly for users and bots. Keep them short, include the most important information and keywords, and make them easy to remember, and you’ll be fine.
Image optimization
You’ll read about it in every SEO beginner’s tutorial. However, sometimes you can forget about it, so for the record – compress your images to be light but still of high quality, and use alt texts, including keywords in them. Image names also matter, so if any of yours are called final_final_5, change them to something more descriptive before publishing.
Did you remember about HTTPS?
Another fundamental, but there are still sites that don’t have it, so be sure to double-check that you have applied HTTPS on your site.
Do you REALLY need to switch to HTTPS?
If you already have an HTTP website and need to switch to HTTPS, remember to set redirects from links from the old version to the new HTTPS.
How to check if your SEO is working?
You already know what things to pay attention to during web development to increase the chance of your website appearing high in search. But how do you know if you’re making progress? Below are some measures to help you see if you are going in the right direction.
Also, remember that the changes you introduce most often will not take effect immediately, and you have to look at your SEO strategy in the long term.
1. Organic traffic
I think this is the most intuitive measure when it comes to checking the effects of an SEO strategy.
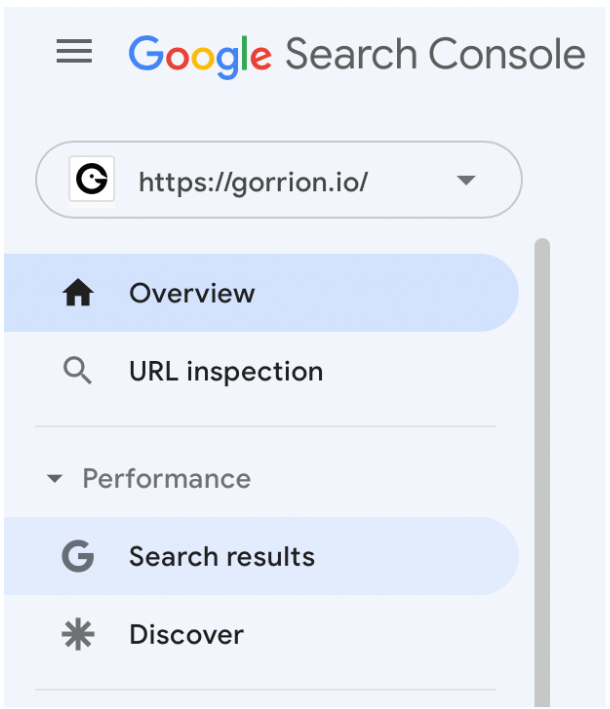
Go to Google Search Console panel, and in the Performance section on the left click Search results. There, you can check how the number of views and clicks on your page from the search engine changed over time.
2. Indexed pages
Pay attention to how many of your pages/URLs have been indexed. Check it from time to time, and when you see a sudden change, it means something is wrong with the page.
Go to your Google Search Console and select the Pages report in the Index section.
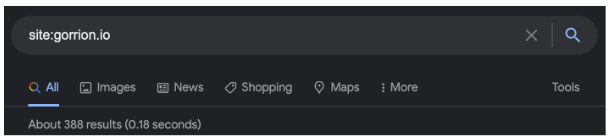
You can also check the approximate number of indexed pages by typing “site:yoursite.com” in Google Search, though it’s better to use the GSC. But hey, isn’t that a way to test your competition?
3. Core Web Vitals
Page experience is an important ranking factor for Google Search and Core Web Vitals are one of the strongest signals (although not the only one!) that your page experience is good. So while keeping the loading scores low will not single-handedly skyrocket your search rankings, they will boost your page experience and give you a better chance of ranking well.
To check on your CWV, go to Google Search Console, and in the Experience section, select Core Web Vitals to find out what the results of your website look like.
4. Website Health Score
I mentioned this in the Technical analysis section (check it to find tools that provide this measure). Your website’s overall score will come in handy for quickly seeing if your SEO efforts are paying off without going into more detailed metrics.
There are many more measures worth paying attention to, but I decided on these four because I know that a web developer probably doesn’t have a lot of time to spend on SEO research in his priorities. The second reason is that these selected measures are closely related to the items I presented earlier and do not require any additional research.
Use technical search engine optimization
As you have already learned, SEO is an extensive topic and includes activities that not only an SEO specialist, or content marketer, can do. Keyword research, link building, and content writing may not apply to you, but you can take care of the technical aspects of SEO. At this point, you probably know there are some technical SEO tasks in which web developers can feel comfortable.
SEO for web developers will help you work on websites for your clients, who will receive a better product from you. You can also use the acquired knowledge to create your own website, which, thanks to appropriate optimization, will be more visible on the web.
What if your website grows and you need a web team to support it? Don’t waste time wandering around; contact us, and we’ll get you the right web development team and help determine what and when to do so that your website is more visible in search and gets valuable organic traffic.
This article was updated in August 2024 to include the latest information and trends in the SEO field, such as new Core Web Vitals.


Have a project in mind?
Let’s meet - book a free consultation and we’ll get back to you within 24 hrs.
Read articles by Monika on web developers' SEO and our special events – Cover Day and Gorrion Unplugged.
Other worthy reads